|
Anapafseos 5 Agios Nikolaos 72100,Crete,Greece,00302841026182,00306932607174,alsfakia@gmail.com
Blog Archive
- ► 2022 (3010)
- ► 2021 (9899)
-
▼
2020
(4138)
-
▼
November
(1979)
-
▼
Nov 11
(96)
- GBE attenuates arsenite‐induced hepatotoxicity by ...
- GDF11 restricts aberrant lipogenesis and changes i...
- Insights into the regulatory role and clinical rel...
- The potential use of theranostic bacteria in cancer
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3329: Current Advances and...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3330: Prognostic Factors I...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3331: Cancer Extracellular...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3332: The Potential of Lon...
- The p.Ser64Leu and p,Pro104Leu missense variants o...
- Novel homozygous truncating variants in ZMYND15 ca...
- A Novel Variant in COX16 Causes Cytochrome c Oxida...
- Aberrant COL11A1 splicing causes prelingual autoso...
- Multiomic analysis elucidates Complex I deficiency...
- A Functional Variant on 20q13.33 Related to Glioma...
- The future of cancer screening
- What matters most: Randomized controlled trial of ...
- Indoor tanning exposure in association with multip...
- Associations of baseline patient‐reported outcomes...
- A multi‐institutional phase 2 trial of stereotacti...
- Tiotropium/Olodaterol Delays Clinically Important ...
- Impact of gastrointestinal symptoms on quality of ...
- Aggravation of Food Allergy by Skin Sensitization ...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3336: The Role of Oxidativ...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3333: Increased PARP Activ...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3335: A Comparative Oncolo...
- Liver tumor F-18 FDG-PET before and immediately af...
- A 5-year-old boy with acute neurological disorder ...
- Antibiotics, Vol. 9, Pages 798: Antimicrobial Resi...
- Grandparental dietary provision, feeding practices...
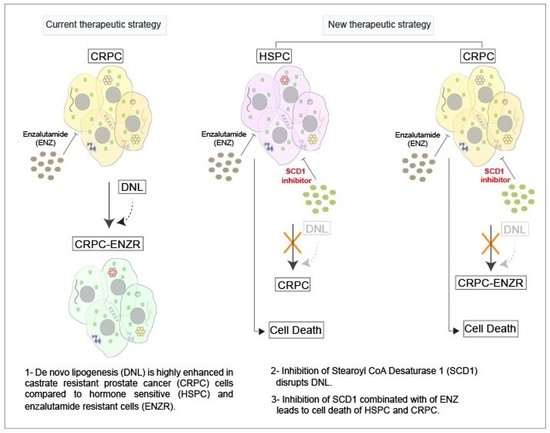
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3339: Modulation of de Nov...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3338: Hydrogen Sulfide-Evo...
- JPM, Vol. 10, Pages 220: Impact of Single-Nucleoti...
- Febuxostat Attenuates the Induction of Vascular Ce...
- Bacterial etiology of sputum from tuberculosis sus...
- Radiological manifestations of thoracic hydatid cy...
- Contralateral Effects of Unilateral Strength and S...
- Treatment of cartilage defects by Low-intensity pu...
- Brain donation
- JFB, Vol. 11, Pages 81: Novel Biofuel Cell Using H...
- Combination of lysine‐specific demethylase 6A (KDM...
- Functional mechanism and clinical implications of ...
- Rapid and Scalable Profiling of Nascent RNA with f...
- A Switch in p53 Dynamics Marks Cells That Escape f...
- Dopamine Inputs from the Ventral Tegmental Area in...
- Generation of universal and hypoimmunogenic human ...
- The roles and functions of Paneth cells in Crohn’s...
- Biosensors, Vol. 10, Pages 173: Electromagnetic Pi...
- Factors Influencing Total Serum IgE in Adults: The...
- Intralymphatic Administration of Metagonimus yokog...
- J. Intell., Vol. 8, Pages 38: A Reappraisal of the...
- Coronary anatomy and comorbidities impact on elect...
- Transcatheter mitral valve thrombosis: A case repo...
- VersaCross transseptal system for transcatheter mi...
- ' ... sciens quia melior est misericordia tua supe...
- The emerging landscape of nanotheranostic-based di...
- JPM, Vol. 10, Pages 221: Fluid Candidate Biomarker...
- Ureterovesical Junction Deformation During Urine S...
- Altered stress field of the human lens capsule aft...
- Hospital bed height influences biomechanics during...
- The effects of exterior boundary conditions on a i...
- Modified SHI‐medium supports growth of a disease‐s...
- Use of Patient-Reported Symptoms from an Online Sy...
- Functional and clinical significance of ROR1 in lu...
- Feasibility of improving patient’s safety with in ...
- EyeDose: An open-source tool for using published M...
- Evidence for interleukin 17 involvement in severe ...
- Non-coding RNA derived from extracellular vesicles...
- Mitochondrial rewiring through mitophagy and mitoc...
- PRMT6 deficiency induces autophagy in hostile micr...
- Modification of diet, exercise and lifestyle (MODE...
- Awake prone positioning of hypoxaemic patients
- Development of a risk prediction model of potentia...
- Development and validity testing of the Adolescent...
- Investigating a new tablet-based telerehabilitatio...
- Discontinuing antidepressant medication after mind...
- Effectiveness of deep electroacupuncture with stro...
- TThe Modification of Diet, Exercise and Lifestyle ...
- Assessing the benefits on quality of life of a mul...
- Current status of radioligand therapy and positron...
- [ASAP] Microenvironment-Triggered Degradable Hydro...
- Flow‐diverting stents in the treatment of peripher...
- Usefulness of updated logistic clinical SYNTAX sco...
- TDP-43 proteinopathies: a new wave of neurodegener...
- Kinetic Modelling and Test–Retest Reproducibility ...
- Aberrant ALOX5 Activation Correlates with HER2 Sta...
- Octreotide Infusion for the Treatment of Congenita...
- Three-Decade Evaluation of Cerebrospinal Fluid Pre...
- Erosion Infiltration in the Management of Molar-In...
- sEMG-Based Neural Network Prediction Model Selecti...
- Establishment and Validation of a Prognostic Risk ...
- The Composition of Gut Microbiota in Patients Bear...
- Use of Argon Plasma Coagulation and Endoscopic Hem...
- The Regenerative Potential of Donkey and Human Mil...
- Biochanin A Mitigates Atherosclerosis by Inhibitin...
- Some Common SNPs of the T-Cell Homeostasis-Related...
- Early Electroacupuncture Extends the rtPA Time Win...
-
▼
Nov 11
(96)
-
▼
November
(1979)
- ► 2019 (2429)
Αλέξανδρος Γ. Σφακιανάκης
Wednesday, November 11, 2020
Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3339: Modulation of de Novo Lipogenesis Improves Response to Enzalutamide Treatment in Prostate Cancer
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)


No comments:
Post a Comment