|
Anapafseos 5 Agios Nikolaos 72100,Crete,Greece,00302841026182,00306932607174,alsfakia@gmail.com
Blog Archive
- ► 2022 (3010)
- ► 2021 (9899)
-
▼
2020
(4138)
-
▼
November
(1979)
-
▼
Nov 05
(91)
- Pediatric craniospinal irradiation with a short pa...
- The record-setting flight of a bat that weighs les...
- Hairy cell leukemia expresses programmed death-1
- An miRNA linked to metabolic disease
- Consistency of variety of machine learning and sta...
- Afatinib‐induced Erosive Pustular Dermatosis of th...
- Treatment considerations for Behçet's disease
- Dendritic cells as predictive markers of responsiv...
- Therapeutic Considerations Related to Stress Level...
- Rehabilitation Of Occlusal Vertical Dimension In A...
- An Alternative Incorporation Technique for Minimiz...
- Feasibility of human spinal cord perfusion mapping...
- Combining chemical exchange saturation transfer an...
- Improved body quantitative susceptibility mapping ...
- Balloon Eustachian Tuboplasty in Pediatric Patient...
- Detection of Respiratory Pathogens Does Not Predic...
- Tip60 protects against amyloid-β-induced transcrip...
- The effect of ketamine on acute and chronic wound ...
- Inhaled Levodopa as a Potential Treatment for Diph...
- Striatal Dopamine Deficit and Motor Impairment in ...
- A New MRI Measure to Early Differentiate Progressi...
- Genome‐Wide Analysis of Copy Number Variation in L...
- A Chlorzoxazone‐Baclofen Combination Improves Cere...
- A POETIC Phase II study of continuous oral everoli...
- Free fatty acid binding pocket in the locked struc...
- Resource conservation manifests in the genetic code
- Untangling the genetics of plasticity
- Genomic architecture of a genetically assimilated ...
- Steering iceberg armadas
- Global food system emissions could preclude achiev...
- Food for thought
- Enigmatic amphibians in mid-Cretaceous amber were ...
- Making peace with the beast within
- The genetic law of the minimum
- Large-area low-noise flexible organic photodiodes ...
- A systematic review of cranioplasty material toxic...
- Evaluating and Comparing Behavioural and Electroph...
- Immediate placement of single implants with or wit...
- Volumetric changes at implant sites: a systematic ...
- Richard Turner-Warwick: the “father of reconstruct...
- Associations between high temperatures in pregnanc...
- NHS offers lung volume reduction procedures for se...
- Erythema migrans mimicking early morphea
- Emergency Department Psychiatric Observation Units...
- 'The Pause: A Second Chance for a Meaningful Conne...
- Paracetamol or nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drug...
- Subcutaneous Rapid‐Acting Insulin Analogs for Diab...
- Unraveling the Crucial Roles of FoxP3+ Regulatory ...
- COVID-19 in Lung Transplant Recipients
- HLA and AB0 Polymorphisms May Influence SARS-CoV-2...
- Summary of International Recommendations for Donat...
- COVID-19 Therapeutics for Solid Organ Transplant R...
- Race, Education, and Gender Disparities in Transpl...
- Peripheral Vascular Disease and Kidney Transplant ...
- Long-term Outcomes After Facial Allotransplantatio...
- Integrative Analysis of Prognostic Biomarkers for ...
- Influence of Sex and Age on Ratings of Confidence ...
- How does the measurement of disability in low back...
- Developing a Framework for Designing and Deploying...
- Circular RNA circTP63 enhances estrogen receptor-p...
- S-allylcysteine induces cytotoxic effects in two h...
- Cryptochrome 1 is modulated by blue light in human...
- Overexpression of Fgf8 in the epidermis inhibits h...
- Paracrine roles of hormone receptors in Riehl’s me...
- Far-Lateral Transcondylar Approach to a Right Cerv...
- A collaborative care psychosocial intervention to ...
- Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving sur...
- Optimal, Large-Scale Propagation of Mouse Mammary ...
- Characterization of Organoid Cultures to Study the...
- Polycythämia vera in der differenzialdiagnostische...
- Magnesium: Bedeutung für die hausärztliche Praxis ...
- Can propranolol act as a chemopreventive agent dur...
- miR-206 as a prognostic and sensitivity biomarker ...
- LncRNA SNHG3, a potential oncogene in human cancers
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3271: Breast Cancer Hetero...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3269: TSPAN1: A Novel Prot...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3270: Integration and Comp...
- Prenatal diagnosis of truncus arteriosus with inte...
- Association between P wave polarity in atrial prem...
- Impact of surgical margin status on the survival o...
- Treatment patterns and medication adherence among ...
- Effects of exergames training on postural balance ...
- '10% of your medical students will cause 90% of yo...
- TOP-ID: a Delphi technique-guided development of a...
- Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy experiences in...
- WeChat-based health education to improve health kn...
- Co-production of an educational package for the un...
- Rationale and study protocol of the Physical Activ...
- Clinical communication in inflammatory bowel disea...
- Incidence and Predictors of Structural Valve Deter...
- Rejuvenated Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cel...
-
▼
Nov 05
(91)
-
▼
November
(1979)
- ► 2019 (2429)
Αλέξανδρος Γ. Σφακιανάκης
Thursday, November 5, 2020
Pediatric craniospinal irradiation with a short partial-arc VMAT technique for medulloblastoma tumors in dosimetric comparison
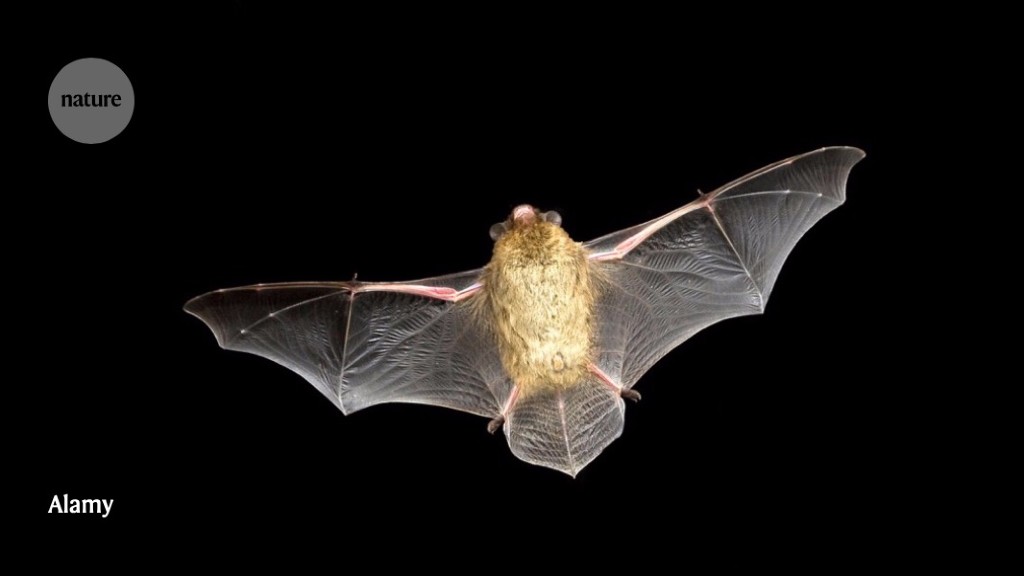
The record-setting flight of a bat that weighs less than a toothbrush
|
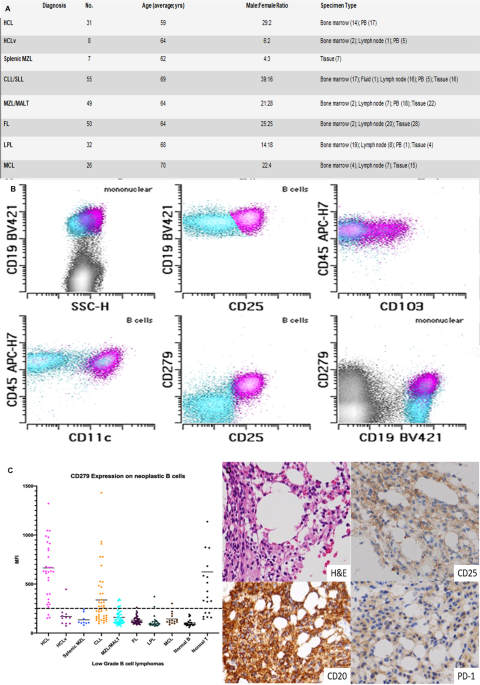
Hairy cell leukemia expresses programmed death-1
|
An miRNA linked to metabolic disease
|
Consistency of variety of machine learning and statistical models in predicting clinical risks of individual patients: longitudinal cohort study using cardiovascular disease as exemplar
|
Afatinib‐induced Erosive Pustular Dermatosis of the Scalp: is there a synergistic effect between EGFR inhibitors and radiotherapy?
|
Treatment considerations for Behçet's disease
|
Dendritic cells as predictive markers of responsiveness to hydroxychloroquine treatment in primary cicatricial alopecia patients
|
Therapeutic Considerations Related to Stress Levels Associated with Hand Eczema: A Clinico‐Etiological Study
|
Rehabilitation Of Occlusal Vertical Dimension In A Patient With Acromegaly: A Clinical Report
|
An Alternative Incorporation Technique for Minimizing Complications in Attachment‐Retained Implant Mandibular Overdentures: Technical Report
|
Feasibility of human spinal cord perfusion mapping using dynamic susceptibility contrast imaging at 7T: Preliminary results and identified guidelines
|