|
Anapafseos 5 Agios Nikolaos 72100,Crete,Greece,00302841026182,00306932607174,alsfakia@gmail.com
Blog Archive
- ► 2022 (3010)
- ► 2021 (9899)
-
▼
2020
(4138)
-
▼
October
(532)
-
▼
Oct 28
(100)
- Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: Glymphedema ...
- Recurrent Orbital Inflammation Secondary to Acute ...
- Optic Nerve Angle in Idiopathic Intracranial Hyper...
- Atypical Ocular Coloboma in Tuberous Sclerosis-2: ...
- Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Character...
- Prevalence of Adrenal Insufficiency and Glucocorti...
- Bilateral Morning Glory Anomaly With Optic Nerve M...
- Comparison of Peripapillary Vessel Density of Acut...
- Optic Nerve Drusen Anterior Displacement and Retin...
- Orbital Apex Syndrome Secondary to Invasive Asperg...
- Neuro-Ophthalmic Manifestations of Sarcoidosis
- Cyclotorsion Measurement on Scanning Laser Ophthal...
- Phosphatidylinositol 4 kinase-β is required for th...
- Phosphatidylinositol 4 kinase-β mutations cause no...
- Angioembolization in intra-abdominal solid organ i...
- New technology‐based assistive techniques in total...
- Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy Is Effective for Patien...
- Pepsin Triggers Neutrophil Migration Across Acid D...
- Operative and Postoperative Complications of Lapar...
- Pediatric laryngopharyngeal reflux
- Ibrutinib treatment via alternative administration...
- Swallowing evaluation by the Kuchikara Taberu Bala...
- MRI-based radiomics to predict lipomatous soft tis...
- Anti-Inflammatory, Barrier-Protective, and Antiwri...
- Sex-Specific Genetically Predicted Iron Status in ...
- Increased Cytoplasmic CD138 Expression Is Associat...
- Circulating Irisin Level and Thyroid Dysfunction
- Modelling Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Cancer
- High uric acid promotes dysfunction in pancreatic ...
- Preoperative imaging for chronic idiopathic coloni...
- Ac2-26 mimetic peptide of annexin A1 to treat seve...
- Breast tumor cells promotes the horizontal propaga...
- Near‐infrared spectroscopy measures of sternocleid...
- Changes in Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) du...
- Detection of microbial contamination based on urac...
- Cavernous Venous Insufficiency: An Underestimated ...
- Protamine Reduces Serious Bleeding Complications A...
- Treating multidrug‐resistant psoriasis with brodal...
- High Frequency of Enterococcal Bloodstream Infecti...
- Prognostic Factors for 30-Day Mortality in Critica...
- Chronic spontaneous urticaria refractory to cyclos...
- Successful treatment of erythematous‐squamous diso...
- Acquired perforating dermatosis
- Sweet Syndrome as an Adverse Reaction to Tyrosine ...
- Functional and aesthetic reconstruction of digital...
- Neck rejuvenation using a noninsulated microneedle...
- Photobiomodulation reduces the impact of radiother...
- Upper Esophageal Sphincter Response to Laryngeal A...
- Genetic Testing Leading to Early Identification of...
- The Effects of Clinical and Home‐based Physiothera...
- Association Between Human Papilloma Virus Infectio...
- Effect of Sleep Surgery on C‐Reactive Protein Leve...
- Botulinum Toxin Injection for Chronic Parotitis
- Colon Cancer Screening Should Start at Age 45
- Botulinum Toxin Injection for Chronic Parotitis
- Phase I study of everolimus, letrozole, and trastu...
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Reporting histol...
- Twin study of neonatal transient-evoked otoacousti...
- Effects of switching from clopidogrel to prasugrel...
- Bilateral Distance Partition of Periventricular an...
- Prospective phase II study of radiotherapy dose an...
- Two parallel worlds of memory T cells
- β‐Lactam Antibiotics in Critically Ill Children
- Non‐syndromic anophthalmia/microphthalmia can be c...
- Clericuzio‐type poikiloderma with neutropenia
- ECHS1 disease .....Developmental delay, regression...
- Robotic Catheterization for Mitral Valve Repair: I...
- Characterization of Circular RNA Transcriptomes in...
- The Erythema Q‐score, an Imaging Biomarker for Red...
- The inflammation in cutaneous lichen planus is dom...
- Immersive Virtual Environments and Wearable Haptic...
- Kigelia africana (Lam.) Benth. fruit extracts in d...
- Mitochondrial cardiomyopathy caused by the mitocho...
- Photosensitivität unter Vemurafenib
- Moderne Therapie der atopischen Dermatitis: Biolog...
- Pilotstudie zum Einfluss von kaltem atmosphärische...
- Comparative accuracy of cone‐beam CT and conventio...
- The right thalamic ventral posterolateral nucleus ...
- Effect of vitamin A, calcium and vitamin D fortifi...
- Combination of a CD26 Inhibitor, G-CSF, and Short-...
- The right thalamic ventral posterolateral nucleus ...
- Trabecular Bone is Increased in a Rat Model of Pol...
- Extrauterine adenomyoma located in the inguinal re...
- A unique case of medulla oblongata epidermoid cyst
- An unusual case of hyalinizing clear cell carcinom...
- Clipping of a basilar tip aneurysm using hypotherm...
- Unusual localizations of hydatid cysts
- To do or not to do: prolapsed, bleeding, rectal po...
- A complicated pulmonary hydatid cyst resembling a ...
- Scalp mass: an atypical presentation of multiple m...
- Unusual disseminated Talaromyces marneffei infecti...
- Hypoxia induces transcriptional and translational ...
- Chromatin Looping Shapes KLF5-dependent Transcript...
- Chemotherapy-Induced Upregulation of Small Extrace...
- Circ_0001421 facilitates glycolysis and lung cance...
- Distinct Genomic Alterations in Prostate Tumors
- Irrespective of the degree of hyperlactatemia, sim...
- Effect of continuous positive airway pressure on g...
- Degos disease
- The feasibility and safety of photoselective vapor...
-
▼
Oct 28
(100)
-
▼
October
(532)
- ► 2019 (2429)
Αλέξανδρος Γ. Σφακιανάκης
Wednesday, October 28, 2020
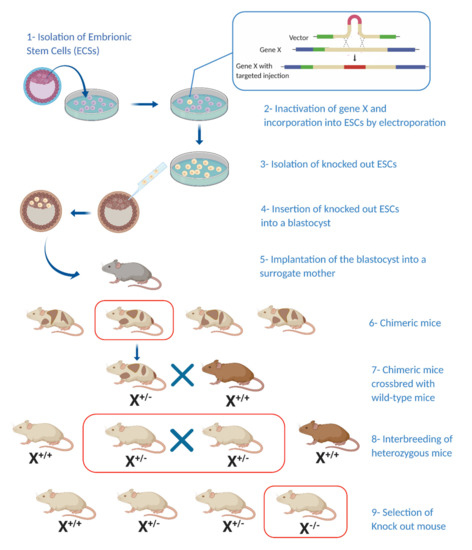
Modelling Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Cancer
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)


No comments:
Post a Comment